Peak Seasons for Supply Chain
As the holidays approach, supply chains experience drastic changes in demand.
Several challenges arise for supply chains at this time, including inaccurate forecasting, weather-related problems, and changes in shopping patterns. As leaders in the field prepare for 2023, it’s valuable to review and plan for peak seasons in the upcoming year.
Read on to learn more about seasonal sales trends and how to stay competitive in today’s market.
Trax transportation spend management solutions play a role in predicting peak season demand. By streamlining data processes, Trax freight auditing solutions improve efficiency, compliance, and visibility, while also reducing unnecessary costs. With the right FAP software, companies won’t be taken by surprise when demand shifts.
What are “Peak Seasons” in Supply Chain?
Peak seasons are the busiest time of the year for supply chains, with the peak shipping season typically beginning at the end of August and continuing through Thanksgiving.
The main reason for this “peak” is holiday shopping. Although the increased demand and sales can be beneficial, there are risks associated with the peak season for shippers. For instance, freight costs are at their highest and inventory is tight.
Average Seasonality
Supply chains experience seasonality when it comes to sales. Essentially, the underlying time-series models sales volumes and goes through a predictable cycle. By accounting for the average seasonality, supply chain leaders can produce better forecasting models.
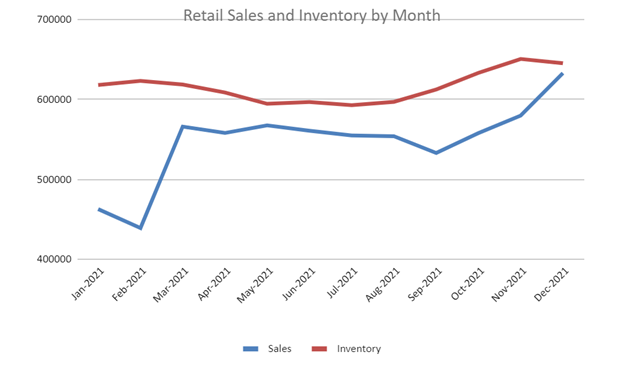
Based on the 2021 data from the Census Bureau, retail sales peak at the end of the year, while inventory doesn’t necessarily adjust accordingly at that time. This leaves companies in a tight spot around the holidays, especially if they didn’t accurately forecast. Supply chain disturbances caused problems for global retailers during the 2021 holidays.
Distortions to Seasonality
There are also distortions to seasonality in the supply chain, also known as the bullwhip effect.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic demand shifted dramatically, which can be seen in the graph above from February 2021-March 2021.
While sales increased by 29% during that period, the inventory decreased by nearly 1%, meaning supply chains didn’t anticipate the effect of declining COVID cases.
The NY Times shows that new cases decreased by about 50% during this time, which is a prime driver for market volatility.
The key is to manage transportation spending effectively during times of uncertainty. By leveraging big data with the proper TSM technology, companies allow for complete visibility into areas of the supply chain that were once siloed.
Breaking down these silos ensures seamless integrations and promotes problem-solving at a higher level.
When to Expect Peak Seasons
Average seasonality can easily be prepared for in the supply chain. By collecting data throughout the year and tracking changes in demand, analysts can predict volatility and prevent the bullwhip effect.
There are specific points during the peak season when companies can specifically expect a surge in demand. Halloween, Thanksgiving, Christmas and New Year's, Black Friday, and Cyber Monday are among the biggest sales drivers during peak season. Knowing this, companies can learn to expect when and how their sales will change during those times.
The only way to expect peak seasons is to study those that have passed. What went well? What went wrong? Asking these questions after the holidays allows companies to identify their mistakes and lessons learned for the following season.
The goal is to make small, continuous improvements throughout the year, which yield substantial results. This is also known as the Kaizen approach. This lean manufacturing methodology emphasizes efficiency.
How to Prepare for Peak Seasons
There are several things that companies can do to prepare for peak seasons in the supply chain:
Better Data Handling
Companies need to normalize and standardize data as it comes in and develop structured processes for analyzing it and deriving insights. In fact, studies show that tools designed to identify major problems and root causes play a vital role in quality control.
Overflow and Storage Handling
There are a few ways to handle peak season overflow, such as optimizing existing space and exploring secondary markets. For instance, a thorough analysis of a company’s current fulfillment space can uncover opportunities for extra shelving, temporary storage space, or even using loading docks for overflow. In addition, expanding to secondary markets for extra storage space is an option, especially for enterprises that know where to expect large distributions.
Optimize and Streamline Operational Processes
Communication silos increase the risk of operational inefficiencies. Talking to carriers and calling suppliers and logistics partners is a solid option for managing inventory during peak season. This allows you to balance inbound and outbound freight more effectively, which optimizes storage space.
A Strong Supply Chain in any Season
Just as you can count on peak season shifts in demand, you can also count on continued market disruption and shifts in consumer behavior as a result. This means that preparing for peak season should not be approached with a “one size fits all” strategy.
The right data management techniques and intelligent visibility into all areas of the supply chain can help you prepare for inventory shortages, storage handling, labor shortages, and other effects of peak season. Contact us today to learn how Trax empowers companies to remain data-driven and achieve TSM maturity.